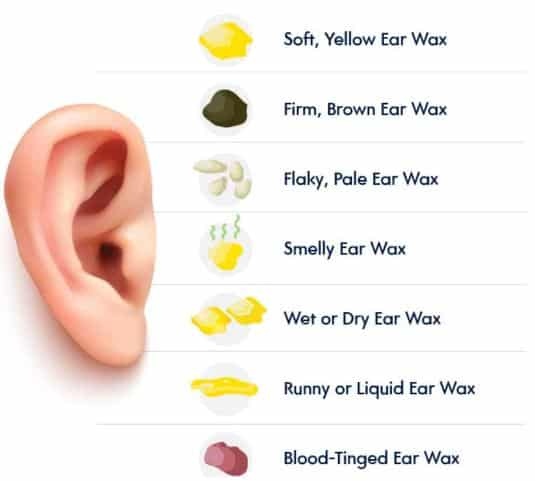
Lets talk ear wax ..........
The color of earwax can vary for several reasons, and these differences are usually normal. Here’s why earwax might appear in different colors:
1. Age of the Earwax
Fresh Earwax: Typically, earwax starts as a light yellow or amber color when it’s newly produced.
Older Earwax: As earwax ages, it can darken, turning brown or even black. This darkening happens because the wax has accumulated more dust, debris, and dead skin cells over time.
2. Oxidation
Exposure to Air: When earwax is exposed to air, it undergoes a process called oxidation, which can cause it to darken. This is similar to how certain fruits, like apples, turn brown when exposed to air.
3. Genetics
Wet vs. Dry Earwax: The color and texture of earwax are partly determined by genetics. People of East Asian descent often have drier, lighter-colored earwax (pale yellow or gray), while those of African or European descent are more likely to have darker, wetter earwax (yellow to brown).
4. Environment and Lifestyle
Dust and Debris: Exposure to dust, dirt, and pollutants can affect the color of earwax, making it appear darker as it traps more particles.
Diet and Health: Although less common, certain health conditions or dietary factors can also influence earwax color.
5. Presence of Blood
Reddish or Black Earwax: Sometimes, earwax can appear reddish or black if there’s a small amount of blood mixed in, usually from a minor injury or irritation in the ear canal. If you notice this and it’s accompanied by pain or other symptoms, it’s a good idea to consult a doctor.
6. Infection or Other Issues
Greenish or White Earwax: While rare, green or white earwax could indicate an infection or the presence of pus, which requires medical attention.
Odor: If earwax is accompanied by a foul odor or unusual color, it may be a sign of an infection or other ear problems.
In general, earwax color variations are normal and usually reflect a combination of factors like age, genetics, and environment. However, if you notice a sudden change in color, especially if it’s accompanied by pain, discomfort, or other symptoms, it’s wise to seek medical advice.